Parasites are normally overlooked in modern medicine when it comes to treating acute and chronic disorders. Therapists and patients alike believe they do not feature in our highly civilised, highly sanitised world. In fact, just the opposite is true – we are importing new stresses through foreign travel and foods from throughout the world against which our organisms often have little or no defence. Consequently, at the very least, parasites are involved in the development of many symptoms and disorders, frequently they are the determining factor in such conditions. This article aims to draw attention to a cause of illness which is largely ignored and to offer a way forward.
- آذر ۱۳۹۷ (۴)
- آبان ۱۳۹۶ (۲)
- تیر ۱۳۹۶ (۱)
- مهر ۱۳۹۵ (۱)
- اسفند ۱۳۹۴ (۲)
- دی ۱۳۹۴ (۴)
- آذر ۱۳۹۴ (۱)
- آبان ۱۳۹۴ (۷)
- مهر ۱۳۹۴ (۸)
- شهریور ۱۳۹۴ (۳)
- مرداد ۱۳۹۴ (۴)
- تیر ۱۳۹۴ (۲۹)
- خرداد ۱۳۹۴ (۱)
- ۹۶/۰۸/۲۰ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS
- ۹۶/۰۸/۱۴The type of Haemoproteus
- ۹۶/۰۴/۲۶Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever
- ۹۴/۱۲/۱۸بیماری و ویروس «کرونا»
- ۹۴/۰۵/۰۶همه چیز در مورد کنه ها
- ۹۴/۰۵/۰۶کک ها (flea) موجوداتی خطرناک
- ۹۴/۰۵/۰۵دلایل شپش سر و درمان آن
- ۹۴/۰۴/۰۵بررسی خانوادههای مختلف سستودها
- ۹۴/۰۴/۰۶فاسیولا (Fasciola)
- ۹۴/۰۴/۰۶توکسوپلاسما وانواع آن
- ۹۴/۰۷/۲۷Trichinella spiralis
- ۹۴/۰۹/۱۸انفلوانزای نوع A
- ۹۴/۰۷/۱۷انتروبیوس ورمیکولاریس (کرمک)
- ۹۴/۰۷/۱۶کرم اسکاریس
- ۹۴/۰۶/۲۶دیپلوستوموم
- ۹۴/۰۷/۱۷Cutaneous larva migrans
- ۹۴/۱۰/۰۹Antimalarial medication
- ۹۴/۰۵/۰۵دلایل شپش سر و درمان آن
- ۹۴/۰۴/۰۶واکسیناسیون در مقابل انگلها
- ۹۴/۰۴/۰۴تب دنگی یک بیماری ویروسی است
- ۹۴/۰۵/۰۶کک ها (flea) موجوداتی خطرناک
- ۹۴/۰۴/۰۱ده انگل درونی انسان
- ۹۴/۰۸/۲۴Bio Resonance Therapy for Parasites
- ۹۴/۰۴/۰۱انگل شناسی تخصصی
- ۹۴/۰۶/۲۸تاریخچه انگل شناسی ماهیان در ایران
- ۹۴/۰۵/۰۶همه چیز در مورد کنه ها
- ۹۴/۰۴/۰۶واکسیناسیون در مقابل انگلها
- ۹۴/۰۴/۰۴تب دنگی یک بیماری ویروسی است
- ۷ آذر ۹۹، ۱۷:۲۹ - حمیدشیستوزما می تواند از راه پوست وارد ...
- ۱ ارديبهشت ۹۸، ۱۳:۳۸ - zahraتوروخدا کمکم کنین من دیگه خسته شدم
- ۶ مرداد ۹۷، ۰۴:۰۳ - camcrush.comI am regular reader, how are you ...
- ۵ آذر ۹۶، ۱۳:۳۶ - یه نفروای من دیگه از دستشون خشته شدم😭😭😭دیگه نمی تونم
- ۹ مهر ۹۶، ۱۵:۵۲ - علیبرای تحقیقم عالی بود
- ۲۱ مرداد ۹۶، ۱۷:۳۵ - حبیبسلام. ممنونم که زحمت کشیدید و این مطلب جامع را فراهم کردید.
- ۱۲ شهریور ۹۵، ۱۷:۳۰ - مریمسلام، این ویدیو رو هم پیشنهاد میدم: http://petmd.ir/node/4
- ۲۴ ارديبهشت ۹۵، ۱۲:۰۹ - حسام الدینلطفا رفرنس رو درج کنید
- ۲۱ دی ۹۴، ۱۸:۴۸ - زهراسلام چطوری میشه کارشناسان وزارت بهداشت تماس گرفت؟
- ۱۴ دی ۹۴، ۰۰:۳۳ - mوزارت بهداشت ازفارغ التحصیلانش ...
- جستجوی تمامی مقالات دنیا
- لیست تمامی کنفرس ها و همایش های دنیا در زمینه های مختلف
- انجمن میکروب شناسی امریکا
- تمامی تست های ازمایشگاهی
- انجمن دکترای علوم آزمایشگاهی تشخیص طبی ایران
- A unifying concept in pathology
- انگل شناسی 2
- Virtual Lab
- Online Virtual Lab Simulations for Science
- ماکت سلولی
- هیستوپاتولوژی
- اناتومی
- انگل شناسی به همراه کوئیز
- اناتومی بدن اسان
- معرفی پایگاه ها و سایتهای علمی
- سازمان سنجش آموزش کشور
- گروه آموزشی دکتر خلیلی
- انجمن علمی انگل شناسی ایران
- سایت دامپزشکان برتر
- وب سایت دکتر( پروفسور) اسماعیل فلاح
- اسلایدهای متنوع قارچ و انگل شناسی
- سایت جستجوی مقالات قارچ شناسی
- سایت جستجوی مقالات وموضوعات میکروبشناسی
- سایت جستجوی مقالات و موضوعات علوم پایه و بالینی
- سایت انگل شناسی مرکز کنترل بیماریها CDC
- Index of fungi pages or photographs on The Net
- سایت های قارچ شناسی
- Dr Sadjjadi's Online Atlas of Parasitology from Shiraz Medical University
- سایت آموزشی و پژوهشی انگل شناسی دانشکده دامپزشکی دانشگاه مشهد
- لینک سایت های مفید در زمینه مالاریا و آنوفل ها
- سایت آزمون دکتری
- دانشکده دامپزشکی دانشگاه تهران
- جامعه مجازی علوم پزشکی کشور
- ادرس سایت برخی از دانشگاه های معتبر جهان و ایران
- لیست سایتهای معتبر علمی دنیا
- مرکز سنجش آموزش پزشکی
- دانشگاه های علوم پزشکی کشور
- پورتال استخدامی کشور
- ثبت نام آزمونهای زبان انگلیسی
- سازمان سنجش آموزش کشور
- دنیای گسترده علوم ازمایشگاهی
- دانشگاه هاروارد
- دانشگاه اکسفورد
- دانشگاه استنفورد
- دانشگاه کمبرج
- دانشگاه کالیفرنیا
- جستجوی هوشمند فراگیر
- دانشگاه فردوسی مشهد
- دانشگاه بوعلی همدان
- انجمن انگل شناسی ایران
- بزرگترین پایگاه علمی زیست شناسی کشور
- مرکز مجازی پژوهش های راهبردی دامپزشکی
- مجله علمی انگل شناسی ایران
- مرکز تحقیقات مقاومتهای میکروبی
- پژوهشگاه رویان
- انجمن علمی قارچ شناسی پزشکی ایران
- انجمن میکروب شناسی ایران
- اطلس پزشکی
- دانلود اطلس های جدید وجالب پزشکی
- پورتال دانشگاه ملایر
- جدیدترین فناوریهای روز جهان
- تازه های اینترنت+اخبار مقالات
- بیوشیمی
- مرکز تحقیقات بیوشیمی و تغذیه
- سایت آزمون دکتری
- وب سایت تخصصی آزمون دکتری
- منابع ازمون دکتری
- کتابخانه ملی ایران
- فنجون
- مرجع دانش سیویلیکا
- پایگاه مقالات علمی
- مرکز تحقیقات مقاومتهای میکروبی
- بیوشیمی
- دنیای گسترده علوم ازمایشگاهی
- پایان نامه و پروژه
- تایپایران - مرکز تخصصی تایپ
This novel bioresonance treatment takes advantage of the energy waves emitted by our body to promote their self-healing and improve their overall functioning naturally, boosting our immune system. Dr. Ines Cremades we respond to frequently asked questions (FAQ) on quantum bioresonance.

What is Bioresonance Therapy?
Bioresonance therapy assesses the energy performance of the human body as a whole. From there, the therapist orders the issuance of necessary bioenergy waves to help cure certain diseases or conditions and help improve the overall performance of our body.
How is Bioresonance Therapy?  It is done through a specific bioresonance machine to fully customize this therapy through the combination of energy and electromagnetic waves frequencies appropriate to the individual needs of each patient.
It is done through a specific bioresonance machine to fully customize this therapy through the combination of energy and electromagnetic waves frequencies appropriate to the individual needs of each patient.
Treatment consists of a first biological general assessment of the health state of the patient from a measurement of energy waves. The measurement is performed in the seven energy sectors in which our body is divided, and is carried out by means of electrodes attached to the patient in three areas of the body: head, hands and feet.
These measurements determine segmented energetic condition of the patient, its responsiveness, chronic conditions, and health status for each sector, allowing even diagnosing specific diseases such as asthma, rheumatism…
After these energy measurements, the therapist analyzes the results obtained by the system and determines the necessary treatment to be applied to improve the health and welfare of the guest, adapting the emission of certain electromagnetic waves to regulate and restore our body function properly.
Bioresonance therapy can be used as add-on to certain health programs such as weight loss, smoking cessation, improved sleep quality, stress regulation, etc. and treatments like lymphatic drainage, cellulite, deep tissue… to enhance their effects.
How reliable bioresonance therapy is?
The effectiveness of bioresonance therapy is proven empirically and is also based on extensive studies and research in the field of biophysics and quantum mechanics which establish the functioning of human body energy. There is scientific evidence that all living things are composed of electromagnetic fields and all biochemical processes are preceded by vibrations and subatomic particles that dictate individual physiological behavior that can be captured by bioresonance apparatus.
How secure bioresonance therapy is? Are there any contraindications?
Bioresonance Treatment is completely safe because the device cannot negatively alter our physiological waves but only help eliminate the pathological ones. In addition, there are no side effects or contraindications, although it is not applicable in people with pacemakers (because the levels would come altered) and, as a precaution, it is not recommended for use in pregnant women.
How long does bioresonance therapy take?
The initial biological screening takes about 20 minutes. After obtaining the results, the therapist will determine how many bioresonance sessions are necessary to obtain the best results.
Related posts:
Enterobius Vermicularis - Pinworm
Human pinworm, Enterobius vermicularis, is the most common parasitic worm infection in the United States and Western Europe. Pinworms are easily transmitted from human to human and are particularly common in children. Luckily the disease, enterobiasis, causes only anal itching.
Enterobius vermicularis does not need an intermediate host to complete its life cycle. Humans get infected by accidentally swallowing or inhaling microscopic pinworm eggs. Once inside the first part of the small intestine, duodenum, pinworm larvae hatch from the eggs. The larvae are only about 0.15 mm long but grow very fast. They migrate towards the ending of the small intestine as they mature into adults. Adults are white, thin worms. Males are 0.2 mm thick and 2–5 mm long whereas females are 0.5 mm thick and 8–13 mm long. Life expectancy for males is seven weeks whereas females live 5–13 weeks. The males usually die after the pinworms have mated in the last part of the small intestine, ileum. The gravid (pregnant) female resides at the beginning of the large intestine, colon, eating what ever food passes through the intestinal tract. Female pinworm reaches fertility within four weeks. She swims at the rate of 12 cm per hour towards the rectum. During sleep when body temperature is low and there is less movement the female pushes out from the anus and lays eggs on the outside skin. The eggs get stuck on skin, underwear or bedding and become infective within a few hours. Eggs survive up to three weeks on clothing, sheets or other objects. After the female has laid 11000–16000 eggs it dies.
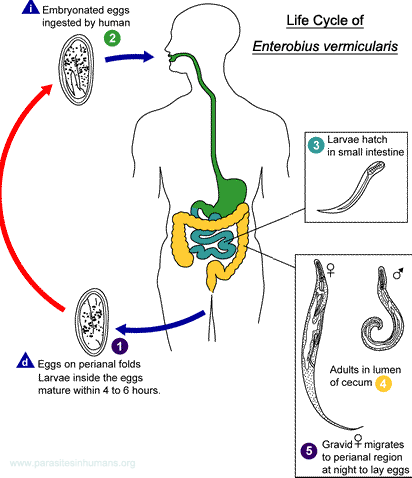
Sometimes pinworms lay eggs inside the colon. If the eggs are not taken out in the feces the larvae might have enough time to hatch. This can only happen in the large intestine or rectum and only if enough oxygen is present. The larvae migrate back up the intestinal tract and develop into adults. This is very rare but happens every now and then.
Diagnosis is made by identifying pinworms or their eggs. Worms can sometimes be seen on the skin around the anus 2–3 hours after falling asleep. Eggs can be collected using a transparent cellophane tape by pressing the sticky side of the tape to the anal skin. The eggs stick to the tape which can be placed on a slide and examined under a microscope by a doctor. Bathing or having a bowel movement can remove eggs from the skin. So this test should be done immediately after waking up. It needs to be repeated on the following two mornings to increase the chance of finding pinworm eggs.
Enterobiasis can be treated with either prescription or over-the-counter medications. A health care provider should be consulted before treating a suspected infection. Some common drugs against pinworms are albendazole and mebendazole. The drugs kill larvae and adults but not the eggs. To get rid of all pinworms another dose needs to be taken after two weeks to kill the newly hatched larvae. All family members should be treated at the same time. If children are in close contact with other children, like in kindergarten, then there is a possibility that other families are infected, too. The least embarrassing way to handle the situation is to only tell the kindergarten teacher. She will inform the other parents that their children might have pinworms and should be treated with the drug.
To prevent new infections always keep fingers out of your mouth and nose. Keep fingernails short and do not bite your nails. Wash your hands after using the toilet and before eating or preparing food. Change clothing, towels, and sheets frequently and wash them in hot water, especially during and after pinworm treatment. If you have pets, keep them clean. The human pinworm, Enterobius vermicularis, does not infect other animals but pets can carry eggs in their fur.
 Also check out the videos.
Also check out the videos.
Pinworm Quiz
To reveal the answer you need to click the correct option.
How big do pinworms grow?
Is enterobiasis easily transmitted from person to person?
How is it diagnosed?
Human infectionbegins with the injection of sporozoites into the bloodstream by infected female Anopheles spp. mosquitoes during a blood meal. Sporozoites travel to the liver and initially invade hepatocytes and multiply, which is known as pre-erythrocytic development. This is followed by the release of merozoites into the bloodstream, which initiates the asexual parasite multiplication stage (see the figure). The variation in the density of asexual parasites in the bloodstream of infected individuals in an area of moderate transmission intensity is shown in red (inset)84. The duration of blood-stage infection is highly variable: many infections are cleared at an early stage, whereas others remain for several months38. A fraction of merozoites form sexual gametocytes, which is the only parasite form that is capable of transmission from humans to mosquito vectors. Immature gametocytes (those in stages I–IV) are sequestered in the bone marrow and only mature gametocytes (stage V) circulate in peripheral blood. The density of mature gametocytes in peripheral blood is typically less than 100 gametocytes per μl of blood (light blue; inset)85 and the vast majority are present at submicroscopic densities. Following ingestion by mosquitoes, each individual gametocyte forms one female macrogamete or up to eight male microgametes. In the mosquito midgut, gamete fusion produces a zygote that develops into a motile ookinete, which can penetrate the midgut wall and form oocysts. Oocyst densities in naturally infected mosquitoes that have fed on either microscopic or submicroscopic parasite carriers are typically in the range of 1–10 oocysts (brown; inset)86. The oocysts enlarge over time and burst to release sporozoites that migrate to the mosquito salivary gland, from where they can infect humans during the next blood meal87.

Epidemiology of gastrointestinal parasites of cattle from selected locations in Southern Ghana
S A Squire, H Amafu-Dey and J Beyuo
Animal Health and Food Safety Division, Council for Scientific and Industrial Research-Animal Research Institute,
P. O. Box AH 20, Achimota, Accra, Ghana
sylbinedu@yahoo.com
Abstract
A cross-sectional study was conducted to establish the prevalence and intensity of gastrointestinal parasites of cattle from two institutional farms located in the Coastal Savanna and Transitional zones of Southern Ghana. A total of 309 (different ages, sex and breed) faecal samples were examined using the McMaster and sedimentation techniques.
Overall, the cattle showed a very high prevalence (95.5%) of parasite infections. Out of this percentage, 75.1% had multiple parasites whiles 20.4% had a single parasite infection. Prevalence of Strongyles (63.1%) was highest, followed by Fasciola (51.1%), Dicrocoelium (39.8%), Eimeria (29.4%), Paramphistomum (25.9%), Schistosoma (21.7%), Ascaris (6.1%) and then Moniezia (2.3%). Strongyles, Ascaris, Moniezia and Eimeria infections were significantly higher (p<0.05) in the calves (0-12 months old) whiles Fasciola, Paramphistomum, and Schistosoma infections were higher (p<0.005) in the adults (>24 months old). In general, most of the animals had low intensity (<500EPG / <10EPC) of infection. There was a wide range of nematodes, cestode and protozoa egg counts (0-47200 OPG, 0-40200 EPG and 0-246000 EPG, respectively). The range of trematodes egg count was 0-52EPC. A wide variety of gastrointestinal parasites were prevalent among cattle in the study area. For effective treatment and control, the variability of parasites would have to be considered. Also, further studies on gastrointestinal parasites dynamics, distribution and impact are proposed.
Key words: coastal savanna zone, intensity, prevalence, transitional zone
Flukes = The Digenea
The Digeneans are a large and successful group of parasites. There are about 6,000 species known to science. They all have complicated life cycles involving at least one intermediate host, which is normally an aquatic snail as well as the primary host which is normally a vertebrate.
Digeneans as adults are flat worm shaped animals, the have two sucker. The first is the oral sucker, around the mouth, this has two functions, a) to hold the animal to its host and b) to assist in feeding. The second sucker is found a little way further down the animals body and it has only a single function, that of attachment.
Life Cycle:
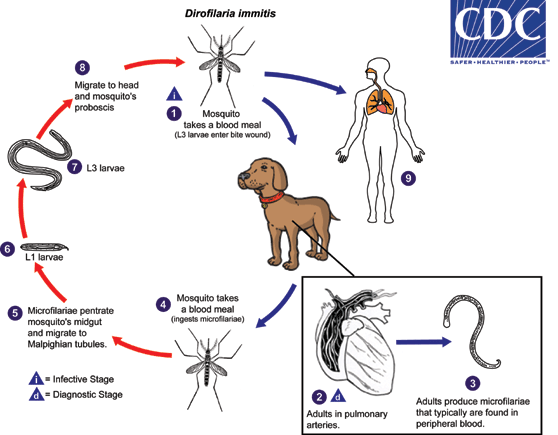
During a blood meal, an infected mosquito (Aedes, Culex, Anopheles, Mansonia) introduces third-stage filarial larvae of Dirofilaria immitis into the skin of the definitive host, which is usually a domestic dog or coyote in the United States (although a wide variety of other animals can also be infected, including felids, mustelids, pinnipeds, beaver, horses, and humans), where they penetrate into the bite wound  . In the definitive host, the L3 larvae undergo two more molts into L4 and adults. Adults reside in pulmonary arteries, and are occasionally found in the right ventricle of the heart
. In the definitive host, the L3 larvae undergo two more molts into L4 and adults. Adults reside in pulmonary arteries, and are occasionally found in the right ventricle of the heart  . Adult females are usually 230-310 mm long by 350 µm wide; males are usually 120-190 mm long by 300 µm wide. Adults can live for 5 - 10 years. In the heart, the female worms are capable of producing microfilariae over their lifespan. The microfilariae are found in peripheral blood
. Adult females are usually 230-310 mm long by 350 µm wide; males are usually 120-190 mm long by 300 µm wide. Adults can live for 5 - 10 years. In the heart, the female worms are capable of producing microfilariae over their lifespan. The microfilariae are found in peripheral blood  . A mosquito ingests the microfilariae during a blood meal
. A mosquito ingests the microfilariae during a blood meal  . After ingestion, the microfilariae migrate from the mosquito’s midgut through the hemocoel to the Malpighian tubules in the abdomen
. After ingestion, the microfilariae migrate from the mosquito’s midgut through the hemocoel to the Malpighian tubules in the abdomen  . There the microfilariae develop into first-stage larvae
. There the microfilariae develop into first-stage larvae  and subsequently into third-stage infective larvae
and subsequently into third-stage infective larvae  . The third-stage infective larvae migrate to the mosquito's proboscis
. The third-stage infective larvae migrate to the mosquito's proboscis  and can infect another definitive host when it takes a blood meal
and can infect another definitive host when it takes a blood meal  . In humans
. In humans  , D. immitis larvae tend to follow the same migratory pathway as in the canine host, ending up in the lungs, where they often lodge in small-caliber vessels, causing infarcts and typical "coin lesions" visible on radiographs
, D. immitis larvae tend to follow the same migratory pathway as in the canine host, ending up in the lungs, where they often lodge in small-caliber vessels, causing infarcts and typical "coin lesions" visible on radiographs




